What Are Dfs Namespace Shared Folders Referred to in Relation to the Virtual Folders?
I of the bones functions provided by enterprise It is the hosting of file services in an arrangement. Since the early days of computer networks, having shared network locations to store and edit documents and other file resource has been a basic requirement.
As the demand for file and network shares gain more and more than momentum, IT admins in many enterprise IT environments found themselves managing numerous file shares, server names, network resources and such but to manage files and network share resources across the arrangement. The management of a large number of network shares across different server resources tin become very labor-intensive.
Microsoft introduced a solution to help organizations deal with and manage file shares across their organization to logically group them into a single hierarchical structure. The technology introduced is known as Distributed File System or DFS.
In this post, we will take a look at what DFS is, how information technology works, requirements and considerations, best practices, and finally, how it is configured.
What is a Distributed File System (DFS)?
Distributed File System or DFS as touched on in the introduction provides the power to logically group shares found on multiple servers and to transparently link shares into a single hierarchical namespace. This is organized in a treelike construction. DFS supports multiple modes including both stand-alone and domain-based DFS services.
Usage of domain-based namespaces is required when you want to provide high availability of the namespace. As with other Microsoft technologies that are replicated along with Agile Directory, with DFS, the topology data for a DFS namespace is stored in Agile Directory.
DFS uses the Windows Server file replication service to copy changes between replicated targets. When users change files stored on one target, DFS replication propagates the changes beyond to the other designated targets in the DFS infrastructure. The nigh contempo changes are preserved.
DFS is an interesting engineering science that abstracts the underlying physical file servers where the actual shares reside, from the namespace of how the shares are accessed. In situations where there may be tens or hundreds of file servers and shares, this tin can become a management nightmare. The DFS namespace aggregates and abstracts this underlying complication from the cease-users.
This is not only beneficial from the end-user perspective only besides the IT admin who, with DFS, has greater flexibility to manage the underlying concrete storage bankroll the DFS hosted shares. If more than storage is needed, the IT admin tin can add a new storage device and share, copy over the files and synchronize them from the one-time device to the new device, and simply retarget the DFS link to point to the new share on the backend.
Does DFS simply work with Microsoft Windows Servers?
A share that is published on a server that is running on a non-Windows Server cannot host a DFS root or provide referrals to other DFS targets. However, not-Windows backed shares can be published for which customer redirectors are bachelor in a DFS namespace. This tin include any SMB-compatible device such equally network-attached storage (NAS) devices from many dissimilar vendors as well as Samba shares. It does not work with NFS or HDFS.
How are DFS namespaces organized?
This is really up to the needs of the business. Mutual DFS organization may be related to the business concern organizational unit of measurement, the geographical location, combinations of both, or perhaps other custom business organisation entities to ascertain a DFS namespace.
What is included with the DFS topology information?
Components of the DFS tree structure include:
- DFS Root – This is a DFS server running the DFS service
- DFS links – DFS links betoken to network shares consolidated in DFS
- DFS Targets – The targets are the actual network shares the DFS links point to
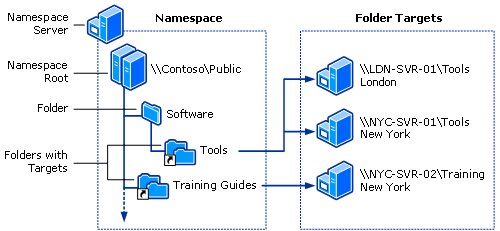
The components making up a DFS namespace include the following:
- Namespace server – This is the DFS server that hosts a namespace. This can exist a fellow member server or a domain controller.
- Namespace root – This is the starting point of the DFS namespace tree. In the case of a domain-based DFS topology, information technology will start with the domain name. With domain-based DFS topologies, the DFS metadata is stored in Active Directory and replicated betwixt the ADDS servers. You can have multiple namespace servers hosting the DFS namespace.
- Binder – There are two types of folders in the DFS namespace – folders without targets and folders with targets. The folders without targets are but for the arrangement of the structure. Folders with targets link to the actual content that stop users can access.
- Folder targets – Folder targets are the bodily UNC paths to a shared binder associated with the folder in a DFS namespace. The folder target is where data is really found. The great matter about domain-based DFS namespaces, the DFS namespace is Active Directory Site aware. If a user in one geographic location accesses the same DFS namespace folder target, they will be directed to the server hosting the data in the same site which enhances the user feel and prevents unnecessary WAN traffic traversing across.
Below are the feature characteristics of the Distributed File Organisation (DFS)
| Feature | Details |
| Type | Windows Server host service |
| Synchronous | Aye |
| Asynchronous | Yes |
| Storage hardware doubter | Aye |
| Replication unit | Volume (Partition) |
| Windows Server Stretched cluster creation | Yes |
| Server-to-server replication | Yes |
| Cluster-to-cluster replication | Yes |
| Non-Windows File Shares | Aye |
| Transport | SMB3 |
| Network | TCP/IP or RDMA |
| Network constraint support | Yes |
| RDMA | iWARP, InfiniBand, RoCEv2 |
| Replication network port | TCP 445 or 5445 |
| Multipath | Yes (SMB3) |
| Kerberos support | Aye (SMB3) |
| Overwrite encryption and signing | Yes (SMB3) |
| Per-volume failovers allowed | Yes |
| Thin-provisioned storage support | Yes |
| Management Tools | PowerShell, Failover Cluster Manager |
Domain-based DFS Namespaces
There are a couple of utilise cases for using the domain-based DFS namespaces.
Nosotros have already touched briefly on why a domain-based DFS namespace would be benign, however, choose domain-based DFS namespaces for the following:
- Is the high-availability for the DFS namespace needed? Use domain-based in this instance. By replicating the namespace between DFS namespace servers, HA is achieved.
- Domain-based DFS namespaces besides provide a actually like shooting fish in a barrel way to abstract the underlying DFS server name by simply presenting the share in the \\< Domain Name >\namespace format. Coupled with Admission-based Enumeration or ABE, users are only presented with the files in a namespace that they have access to.
To use the domain-based DFS namespace topology:
- Brand certain your Active Directory woods functional level is Windows 2008 or college
- Domain functional level needs to be at Windows Server 2008 or college
- Namespace servers must be running Windows Server 2008 or higher
How Distributed File System (DFS) Works
A central component to the DFS working is DFS Replication.
DFS Replication in Windows Server is a role service that allows replicating the folders referred to by a DFS namespace path across multiple servers and sites. DFS replication is configured as a multi-master replication engineering meaning whatever member of the DFS replication grouping tin can make changes to the information.
DFS replication makes apply of an efficient pinch algorithm called Remote Differential Compression (RDC) to observe changes to information. RDC is extremely efficient in that it can detect changes to a file and only copy the changed file blocks instead of recopying the entire file.
A DFS replication group mentioned before is a grouping of servers that participates in the replication of one or more replicated folders. A replicated folder stays synchronized between the members included in the DFS replication group. The advice between the various DFS replication group members forms the DFS replication topology.
The settings for the replication grouping including its topology, schedule, and bandwidth throttling are applied to the replicated folders contained in the DFS replication grouping.
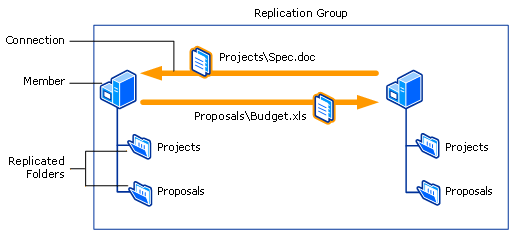
Each replicated folder in the DFS replication group has unique settings including the file and subfolder filters to filter out different files and subfolders for each replicated binder. Replicated folder can be located on different volumes in the member and do non need to be shared folders or part of a namespace. DFS Replication can be managed by using the DFS Management console, DfsrAdmin and Dfsrdiag commands or scripts that phone call WMI.
An important note to consider when looking at how DFS replication works is that DFS replicates a file simply after it is closed. This means that it is not a suitable solution for replicating files that may constantly exist in apply like database files or other files that are open up for an extended period of fourth dimension. For documents or other files that need to exist worked on in parallel with other users, yous may want to look into other technologies like Storage Replica that was introduced in Windows Server 2016.
Distributed File System (DFS) Requirements
There are a few requirements and considerations to make annotation of when thinking of deploying a Distributed File Organisation (DFS).
Servers that are running the following operating systems can host multiple domain-based namespaces in addition to a unmarried stand-solitary namespace.
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter and Enterprise Editions
- Windows Server (Semi-Annual Aqueduct)
Servers that are running the following operating systems can host a single stand-alone namespace:
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard (Windows Server 2008/R2 are at end of extended support.
What are the requirements to host a DFS namespace?
| Server Hosting Stand-Lonely Namespaces | Server Hosting Domain-Based Namespaces |
| An NTFS is required to host a DFS namespace | Must contain an NTFS volume to host the namespace. |
| Either member servers or domain controllers tin can be used | Must be a member server or domain controller in the domain in which the namespace is configured. (This requirement applies to every namespace server that hosts a given domain-based namespace.) |
| Failover clusters tin be used for high availability to host the DFS namespace for resiliency | The namespace cannot exist a clustered resource in a failover cluster. However, you can locate the namespace on a server that also functions as a node in a failover cluster if yous configure the namespace to use only local resources on that server. |
What are the requirements to deploy DFS replication?
- Update the Agile Directory Domain Services (ADDS) schema to include Windows Server 2003 R2 or after schema additions. No read-just replicated folders with the Windows Server 2003 R2 or older schema additions.
- All servers in a DFS replication group must be located in the same Agile Directory forest. You cannot enable replication across servers in unlike AD forests.
- Install DFS Replication on all servers that will human activity as members of a replication grouping.
- Ensure you have the proper antivirus exceptions in place for DFS replication as these can trigger faux positives in many antivirus solutions.
- Locate folders that you want to replicate with DFS on NTFS formatted volumes. As of yet, DFS Replication does not back up the Resilient File Organization (ReFS) or the FAT file system. DFS Replication also does non back up replicating content stored on Cluster Shared Volumes.
Considerations in Using Distributed File Organisation (DFS) with Azure
DFS can be used in conjunction with Azure, but there are a few considerations that you volition want to make in using the two together. It has been tested as documented by Microsoft to utilise DFS with Azure virtual machines.
Below are a few points to note with DFS and Azure:
- No clustering of stand-alone namespaces in Azure VMs
- Domain-based namespaces can be run on Azure VMs, including Azure environments running Azure Agile Directory
- Using snapshots or saved states to restore VMs DFS Replication causes DFS Replication to fail, which can crave special database recovery steps.
- Don't export, copy, or clone DFS Replication VMs
- Use fill-in software from inside the guest virtual auto
- You will need to take a site-to-site VPN connectedness between your on-bounds replication group members and members hosted in Azure VMs with advisable firewall port exceptions for communication between them. This includes RPC Endpoint Mapper (port 135) and randomly assigned ephemeral ports.
Configuring Distributed File Arrangement (DFS)
Let's have a wait at how to configure Distributed File Organisation in Windows Server 2019.
To install the Distributed File System DFS on a Windows Server, information technology involves calculation a function to your servers. The DFS roles are really a subcomponent of the File and Storage Services role.
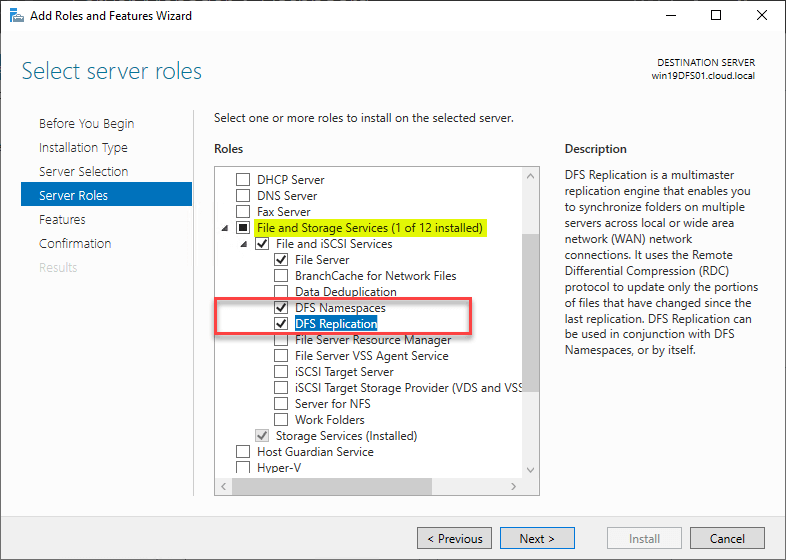
Below is a wait at the available DFS roles when using the Get-WindowsFeature PowerShell cmdlet.
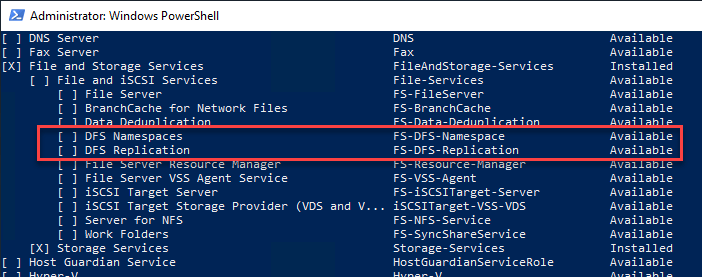
You lot tin install the DFS roles by using either the Server Manager console or using PowerShell.
PowerShell is a great fashion to install DFS roles apace and hands. This is too great for the automation and mass installation of roles across many servers.
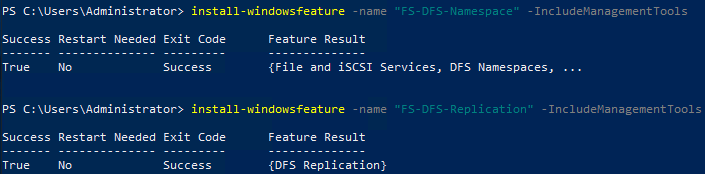
- Install-WindowsFeature -name "FS-DFS-Namespace" -IncludeManagementTools
- Install-WindowsFeature -name "FS-DFS-Replication" -IncludeManagementTools
Creating a DFS Namespace
Yous can launch the DFS Management Panel by using the command dfsmgmt.msc.
As yous can run across the direction console is fairly straightforward. Under the Actions pane, you can click the New Namespace button to begin creating a new DFS namespace.
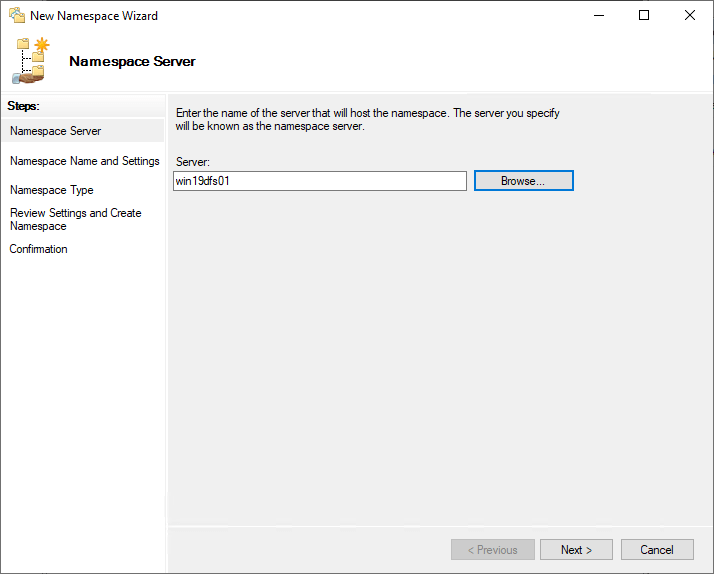
The New Namespace Sorcerer launches. The first step is inbound the name of the server that will host the namespace. You tin either enter the server name or click Browse and find the server name.
Enter the Namespace Name and Settings. As noted, the proper name you lot choose is the name that appears after the server or domain name in the namespace path. You lot tin can also click the Edit Settings push button and become more granular with the local path and settings.
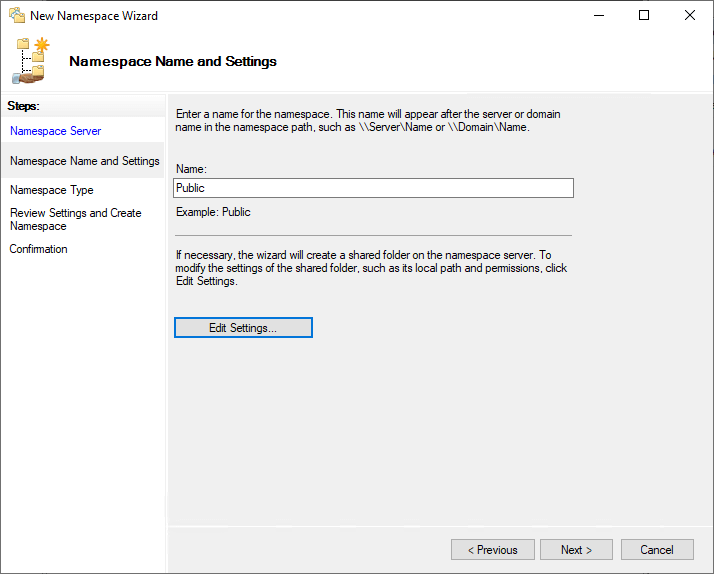
The next step is choosing a Namespace Type. This is where you can choose betwixt a domain-based and a standalone namespace server. Also, you can cull the Enable Windows Server 2008 mode (enabled by default) which sets up the namespace with increased scalability and access-based enumeration ABE. ABE means that end users only see the files presented which they have access to.
Cull stand-alone namespace, if:
- Your organization does not apply Active Directory Domain Services (Advertizing DS).
- You lot use the failover cluster to increase the availability of the namespace.
- You want to create a unmarried namespace with more than 5,000 DFS folders in a domain if y'all don't meet the requirements for a domain-based namespace(Windows Server 2008 mode).
The following minimum requirements to the Windows Server 2008 mode
- The wood uses the Windows Server 2003 or college forest functional level.
- The domain uses the Windows Server 2008 or higher domain functional level.
- All namespace servers are running Windows Server 2008 and afterwards.
Choose domain-based namespace, if:
- Y'all utilise multiple namespace servers to ensure the availability of the namespace.
- Yous desire to hibernate the name of the namespace server from users.
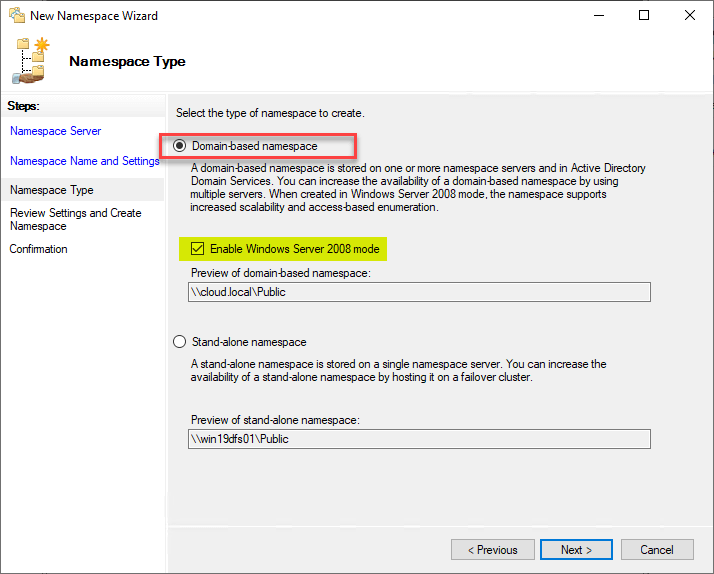
Review the settings and create the namespace.
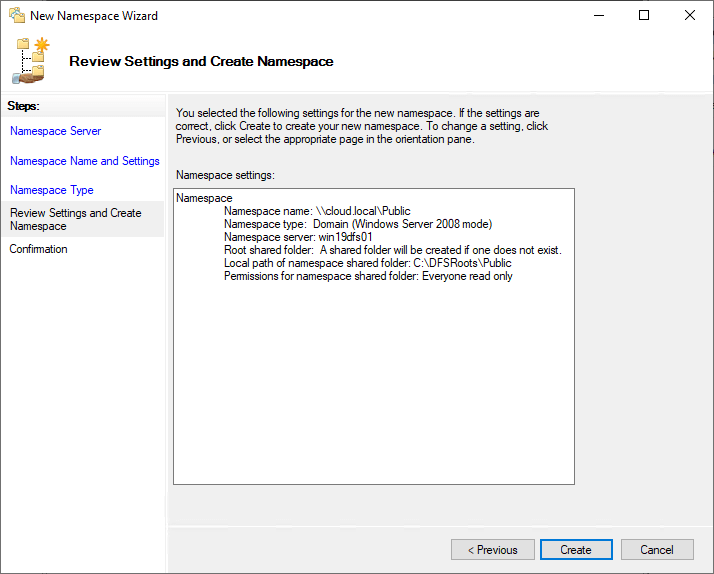
The create namespace magician completes successfully.
Calculation a DFS Target to a Namespace
Side by side, we need to add a target to the DFS namespace. Right-click the namespace and choose New Folder.
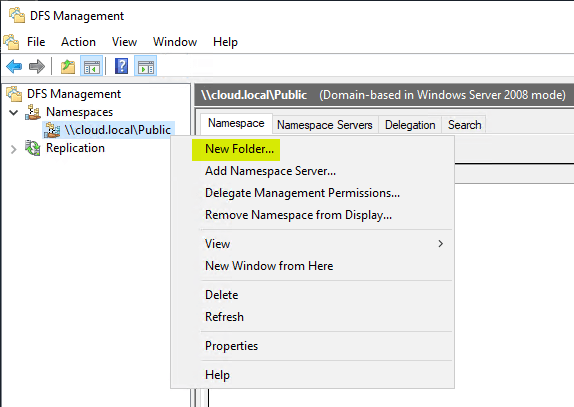
Click Add together.
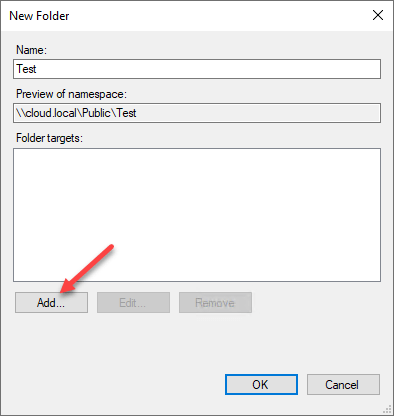
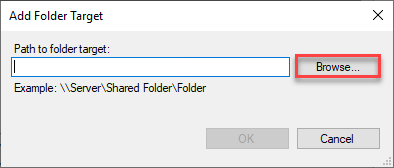
Y'all can enter either a UNC path for a remote server share, or y'all tin can click the Browse button and select a local server folder.
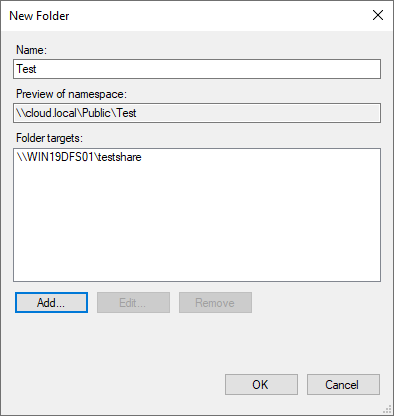
Here, we have added a local binder.
Creating a New Replication Group
Finally, let's walk through creating a replication group that will replicate the source DFS housed folder to the target server. This will copy the data from the source to the destination.
***Note*** files are not replicated until they are closed.
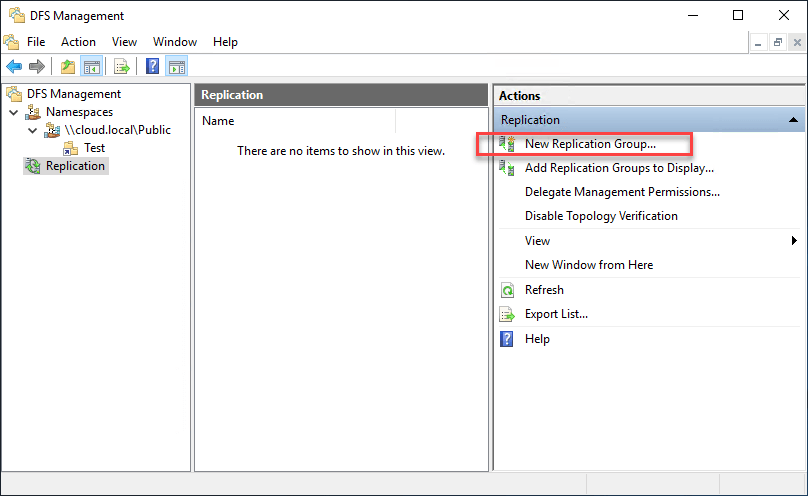
Choose the Replication Group Blazon.
Cull the 'Multipurpose replication group' if yous would like to configure custom replication topologies. It too allows you to create a custom replication topology by kickoff adding a ready of servers to the replication group and then configuring custom connections betwixt them to accomplish the desired custom replication topology.
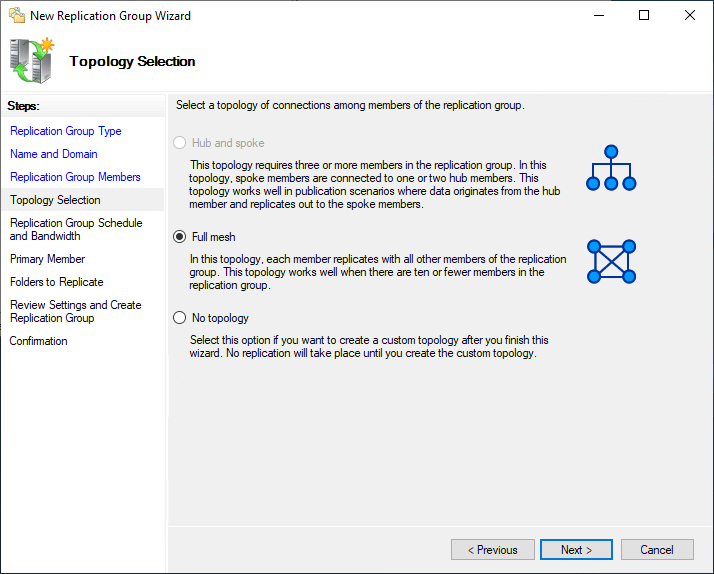
There are three options available under the Multipurpose replication group: Hub and spoke, Total mesh and No topology.
Hub and spoke
It can be used with three or more servers. Each spoke can use one or more than hub members to replicate data. Multiple hubs can be used for redundancy in case any one of them becomes unavailable. Hubs should host the same replication data.
Full mesh
Information technology can be used betwixt two or more than servers. In a full mesh topology, data is replicated between all replication members. It's recommended that you always use this topology if the DFS replication group is composed of less than 10 servers.
No topology
You lot will exist able to enable DFS connections once the wizard is completed. No replication will occur until the connections are configured.
Choose the 'Replication group for data drove', if you want to add together 2 servers to a replication group in such a style that a hub (destination) server can exist configured to collect data from some other branch server. You cannot keep on calculation new members to a data collection replication group, merely you tin keep on creating additional replication groups that all take the same hub server, to make up a kind of hub and spoke topology if you had multiple 'branch offices.'
Multipurpose Replication Group is a more versatile setup and tin can operate in hub or mesh mode. If you're not sure what to selection, pick a Multipurpose Replication Group.
Here we are choosing a Multipurpose replication group. This option configures replication betwixt 2 or more servers for publication content sharing and other scenarios.
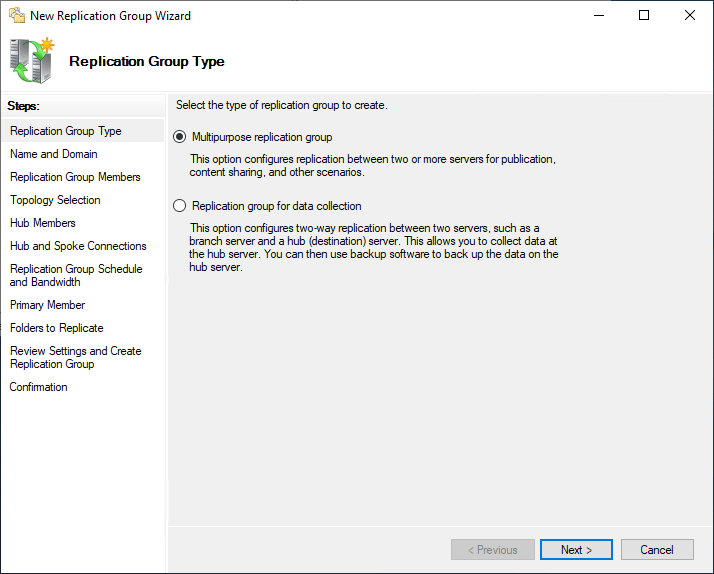
Choose the Name and Domain.
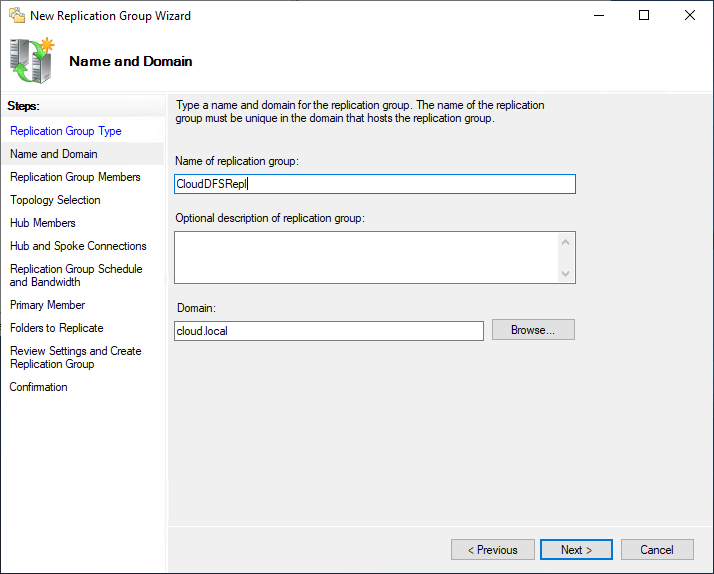
Cull the Replication Group Members. Hither nosotros have selected the 2 DFS servers we want to include in the Replication Group.
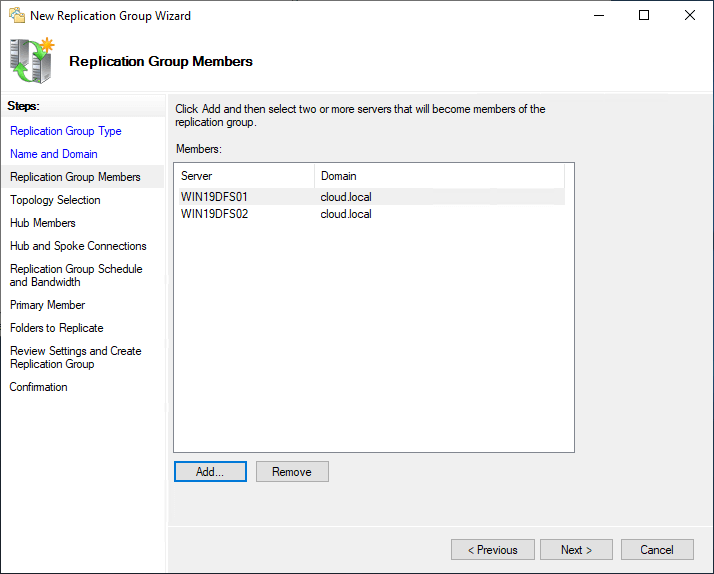
Side by side, you cull the Replication Topology. If y'all take only 2 servers, the Hub and Spoke selection is greyed out. By default, with two servers, you will see Total Mesh selected.
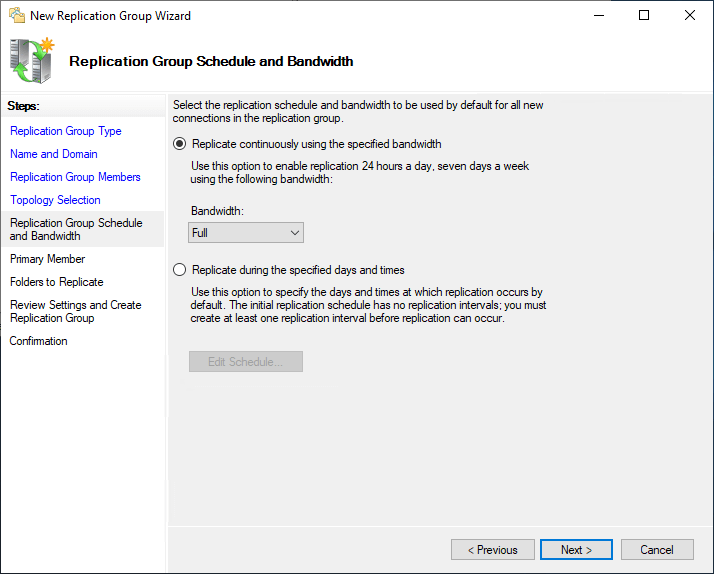
With DFS Replication, you tin choose the replication schedule and the bandwidth yous want to allocate to the DFS replication process.
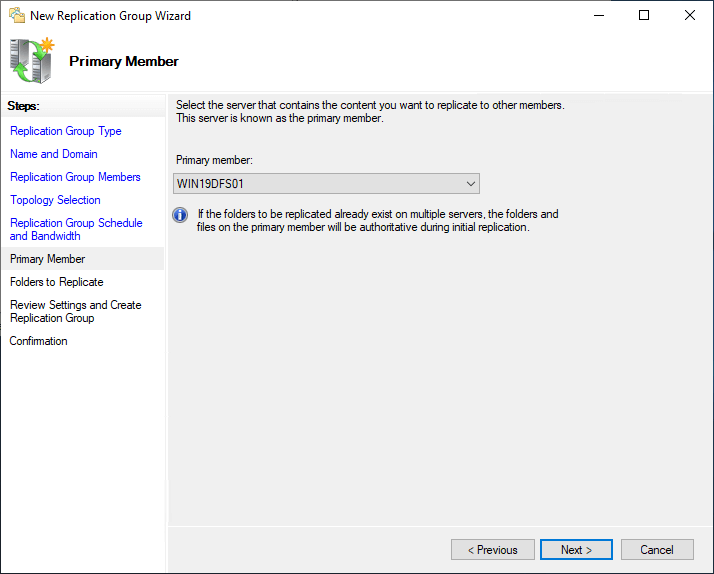
Select the Main Member for the DFS Replication grouping.
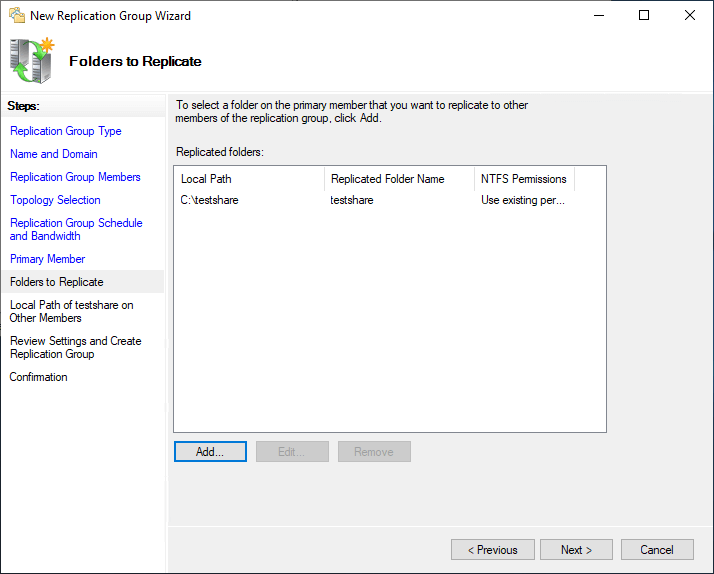
Cull your folders to replicate to the replication members. Click the Add push button to add these folders.
Cull the local path on the replication members where the replicated binder volition be replicated.
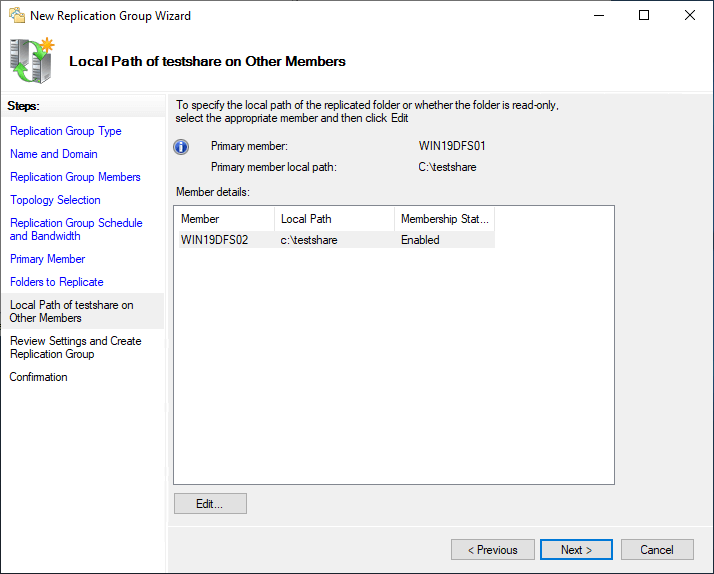
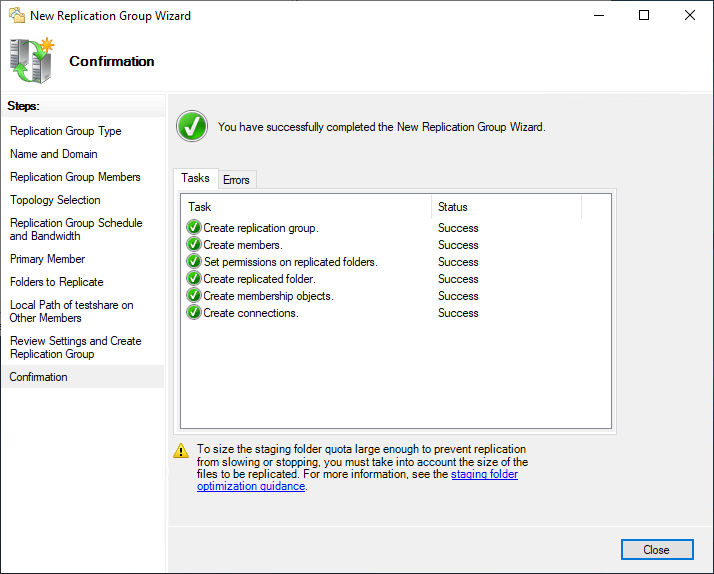
Review the Replication Settings and click Create to create the replication group.
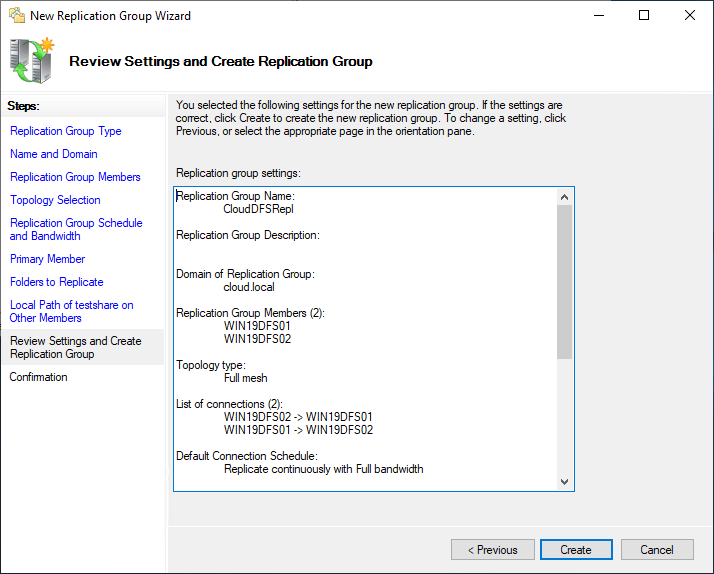
Replication grouping is created successfully.
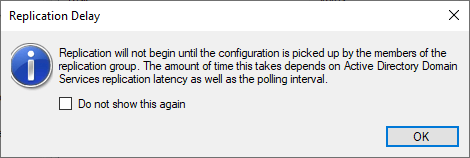
You lot will see an advisory bulletin about the possible replication delay.
Later only a few moments, the source file is replicated to the DFS replication member. Below, a file was created on the source server and inside a few moments, the file had replicated to the DFS replication grouping fellow member, with the aforementioned contents.
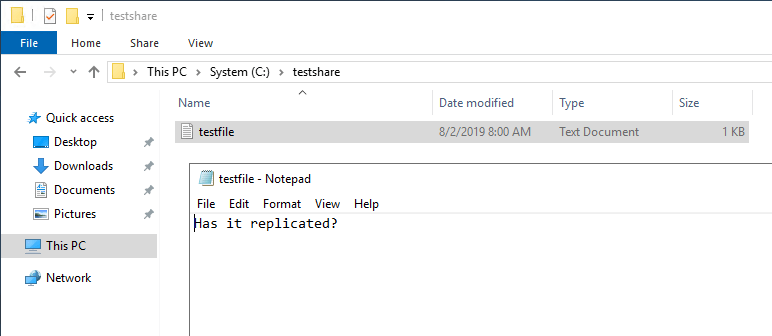
DFS Does Non Supercede Backups
At that place could be a misconception about DFS and its utilize cases to assume that DFS would serve as a form of backup since information can be replicated betwixt a number of replication members in the DFS replication group. However, go along in heed, while the replication process tin can replicate data that would serve to create additional copies of data on additional servers, this does non protect from data loss as a result of end-user mistakes and security threats similar ransomware.
Due to the replication process, changes made by end-users or ransomware would be replicated to the other servers in the DFS replication group. Businesses still need to backup their data and keep multiple restore points adjustment with business needs, to truly protect their data.
Vembu BDR Suite provides a peachy solution for businesses and their data. It allows granular restores of data down to individual files and folders.
Additionally, information technology globally protects your data past creating backups of VMs as well equally physical machines that may exist backing concern-critical services.
Be sure to download a fully-featured trial version of Vembu BDR Suite hither.
Wrapping Up
Windows Distributed File Arrangement (DFS) is a bang-up style to scale many Windows Server file shares across a network. It allows easily aggregating file shares logically and abstracting the namespace from the bodily underlying network share name. This can arrive much easier for end-users to reach resources and for IT admins to perform maintenance on the underlying storage contributing to the shares.
The process to create a DFS namespace, add target shares/folders, and create replication groups is very straightforward using either GUI or command-line options including PowerShell to command DFS. DFS is not a backup solution for your data. While it can replicate information to multiple servers, this does not protect your business from stop-user related data loss or information loss as a effect of cybersecurity threats like ransomware.
Using a modern backup solution like Vembu BDR Suite is a corking style to ensure your data is condom and protected from the terminate user or cybersecurity threats. Using tools similar DFS combined with a fill-in solution that can properly protect your information, you tin be confident in the security, resiliency, and recoverability of information despite any threats that may come along.
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.
Source: https://www.vembu.com/blog/distributed-file-system-dfs-windows-server-2016-brief-overview/



Post a Comment for "What Are Dfs Namespace Shared Folders Referred to in Relation to the Virtual Folders?"